程序结构
- 命名空间声明
- Class类
- Class方法
- Main方法
- Statements & Expressions
- 注释(/* 多行注释 */ //单行注释)
- 文件后缀:.cs
Tips:
- C#语法对于大小写是敏感的
- 所有语句和表达式必须以;结尾
- 从Main方法开始执行
- 文件名可以和类名不同
基本语法
using关键字
1 | using System |
class关键字
特性
- 用于声明一个类
- 类中会包含成员变量和成员函数
- 类的调用需要在Main方法中实例化
命名规则
- 标识符必须以字母、下划线或 @ 开头,后面可以跟一系列的字母、数字( 0 - 9 )、下划线( _ )、@。
- 标识符中的第一个字符不能是数字。
- 标识符必须不包含任何嵌入的空格或符号,比如 ? - +! # % ^ & * ( ) [ ] { } . ; : “ ‘ / \。
- 标识符不能是 C# 关键字。除非它们有一个 @ 前缀。 例如,@if 是有效的标识符,但 if 不是,因为 if 是关键字。
- 标识符必须区分大小写。大写字母和小写字母被认为是不同的字母。
- 不能与C#的类库名称相同。
关键字
保留关键字:
abstract as base bool break byte case catch char checked class const continue decimal default delegate do double else enum event explicit extern false finally fixed float for foreach goto if implicit in in(generic modifier) int interface internal is lock long namespace new null object operator out out(generic modifier) override params private protected public readonly ref return sbyte sealed short sizeof stackalloc static string struct switch this throw true try typeof uint ulong unchecked unsafe ushort using virtual void volatile while
上下文关键字:
add alias ascending descending dynamic from get global group into join let orderby partial(type) partial(method) remove select set
数据类型
- 值类型(Value types)
- 引用类型(Reference types)
- 指针类型(Pointer types)
值类型
从类System.Value.Type中派生,包含数据,如int,char,float
- bool,布尔值,True或False,默认False
- byte,8位无符号整数,0-255,默认0
- char,16位Unicode字符,U+0000-U+ffff,默认’\0’
- decimal,128位精确的十进制值,默认0.0M
- double,64位双精度浮点型,默认0.0D
- float,32位单精度浮点型,默认0.0F
- int,32位有符号整数类型,-2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647,默认0
- long,64位有符号整数类型,默认0L
- sbyte,8位有符号整数类型,-128到127,默认0
- short,16位有符号整数类型,-32768到32767,默认0
- uint,32位无符号整数类型,0 到 4,294,967,295,默认0
- ulong,64位无符号整数类型,默认0
- ushort,16位无符号整数类型,0到65535,默认0
引用类型
- 不包含存储在变量中的实际数据,但包含对变量的引用
- 具体是指一个内存位置,使用多个变量时,可以指向一个内存位置
- 内置的引用类型:object,dynamic,string
Object类型
- CTS中所有数据类型的终极基类
- 全称是:System.Object
- 可以分配其它任何类型的值,但需要先进行类型转换
- 当一个值类型转换为对象类型时,被称为装箱
- 当一个对象类型转换为值类型时,被称为拆箱
- 发生于编译时
Dynamic类型
- 可以存储任何类型的值
- 发生于运行时
1
2// 语法结构:
dynamic <variable_name> = value;
String类型
- 可以给变量分配任何字符串值
- 全称是:System.String
- 从对象类型中派生而来
- 其值的分配方式有两种:引号和@引号
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14// 引号字符串:
String str = "Hello.";
// @引号字符串:
@"Hello.";
// @字符串的特殊用法:
// 可以将转义字符当作普通字符对待
String str2 = @"C:\Windows";
// 等价于
String str2 = "C:\\Windows";
// 可以任意换行,换行符及缩进空格都计算在字符串长度之内
String str3 = @"<script type=""text/javascript"">
<!--
-->
</script>";
类型转换
- 两种转换方式:隐式转换和显示转换
隐式转换
定义:指将一个较小范围的数据类型转换为较大范围的数据类型时,编译器自动完成的类型转换,默认以安全的方式进行,不会导致数据丢失。
举个栗子:
从小的整数类型转换为大的整数类型,从派生类转换为基类。
1 | byte a = 1; |
显示转换
定义:指将一个较大范围的数据类型转换为较小范围的数据类型,或者将一个对象类型转换为另一个对象类型时,需要使用强制类型转换符号进行显示转换,会造成数据丢失。
举个栗子:
将一个int类型变量赋值给byte类型。
1 | int i = 1; |
类型转换的方法
- ToBoolean: 将类型转换为布尔型
- ToByte: 将类型转换为字节类型
- ToChar: 将类型转换为单个Unicode字符类型
- ToDateTime: 将类型(整数或字符串类型)转换为日期-时间结构
- ToDecimal: 将浮点型或整数类型转换为十进制类型
- ToDouble: 将类型转换为双精度浮点型
- ToInt16: 将类型转换为16位整数类型
- ToInt32: 将类型转换为64位整数类型
- ToSbyte: 将类型转换为有符号字节类型
- ToSingle: 将类型转换为小浮点数类型
- ToString: 将类型转换为字符串类型
- ToType: 将类型转换为指定类型
- ToUInt16: 将类型转换为16位无符号整数类型
- ToUInt32: 将类型转换位32位无符号整数类型
- ToUInt64: 将类型转换为64位无符号整数类型
变量
基本值类型的分类:
- 整数类型:sbyte,byte,short,ushort,int,uint,long,ulong,char
- 浮点型:float,double
- 十进制类型:decimal
- 布尔类型:true,false,自定义的值
- 空类型:可为空值的数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// 语法定义:
[][variable_name] = value;
// System.Console
// ReadLine()
int num;
num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
// 将用户输入的数据转换为int数据类型,因为Console.ReadLine()只接受字符串格式的数据。
常量
- 常量是固定的值,程序执行期间不会改变
- 常量可以是任何基本数据类型
- 常量可以被当作常规的变量
浮点常量
- 使用浮点形式表示时,必须包含小数点、指数或同时包含两者
- 使用指数形式表示时,必须包含整数部分、小数部分或同时包含两者
- 有符号的指数是用 e 或 E 表示的
字符常量
- 通常括在单引号里,可以存储在一个简单的字符类型变量中
- 可以是一个普通字符’x’,一个转义序列’\t’,一个通用字符’\u02C0’
常用的转义字符: - \\ \字符
- \‘ ‘字符
- \“” “字符
- ? ?字符
- \a Alert或bell
- \b 退格键
- \f 换页符
- \n 换行符
- \r 回车
- \t 水平制表符
- \v 垂直制表符
- \ooo 一到三位八进制数
- \xhh… 一个或多个数字的十六进制数
字符串常量
- 通常括在双引号里,或括在@””里
- 可以将一个很长的行拆成多个行,可以使用空格分隔各个部分
定义常量
1 | // 语法: |
运算符
算数运算符
- +
- -
- *
- /
- %
- ++ (a++,先赋值再加)(++a,先加再赋值)
- -- (a–,先赋值再减)(–a,先减再赋值)
关系运算符
- ==
- !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
逻辑运算符
- && 同为true则结果为true
- || 任意一个结果为true则结果为true
- ! 反转
位运算符
略
其它运算符
- sizeof(),返回数据类型的大小
- typeof(),返回class的类型
- &,返回变量的地址
- *,变量的指针
- ?:,条件表达式,条件为真则为X,否则为Y
- is,判断对象是否为某一类型
- as,强制转换,即使转换失败不会抛出异常
优先级
- 有括号先括号
- 后乘除再加减
- 然后位移再关系
- 逻辑完后匹条件
- 最后一个小逗号
判断
- if
- if … else
- if嵌套
- switch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19switch(expression){
case constant-expression:
statement;
break;
case constant-expression:
statement;
break;
...
default:
statement;
break;
}
//expression必须是一个整型或枚举类型或者是一个class类型(且该class有一个单一的转换函数可以将其转换为整型或者枚举类型)
//case的数量可以任意,每个case后需要冒号结尾
//当定义的变量等于case后面的常量,则statement会被执行,直到break
//不是每个case都需要break,当case语句为空时可以不包含break
//C#不允许从case部分继续执行到下一个case部分,如果case语句中有已经执行,则必须包含break或其它跳转语句
//可以有一个可选default的语句,在switch结尾,当所有case都不为true时执行
//如果要从一个case显示贯穿到另一个case,可以使用goto - switch嵌套
循环
- while
1
2
3while(condition){
statement;
} - for/foreach
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// for
for(init; condition; increment){
statement;
}
// foreach
foreach(var item in collection){
...
}
// 主要用于迭代数组或一个集合对象,如数组、列表、字典等 - do … while
1
2
3
4do{
statement;
}while(condition);
// 先执行语句再判断条件 - 嵌套循环
- break,终止switch中的case,终止循环
- continue,跳过本轮循环,开始下一轮循环
封装
定义:将一个或多个项目封闭在一个物理的或者逻辑的包中。
抽象和封装是面向对象程序设计的特性,抽象允许相关信息可视化,封装则实现所需级别的抽象。
访问修饰符
- public:所有对象都可以访问,即任何公有成员都可以被外部类访问
- private:对象本身在对象内部可以访问,即同类中的函数可以访问它的私有成员,包括类的实例也不能访问
- protected:只有该类对象及其子对象可以访问,主要用于继承
- internal:同一个程序集的对象可以访问即可以被定义在该成员所定义的应用程序内的任何类或方法访问
- protected internal:访问限于当前程序集或派生自包含类的类型,主要用于继承
- 如果没有指定访问修饰符,则使用类成员的默认访问修饰符,即private
方法
定义
一个方法是将一些相关的语句组织在一起,用来执行一个任务的语句块。
1 | <Access Specifier><Return Type><Method Name>(Parameter List){ |
参数传递
- 值参数:复制参数的实际值给函数的形式参数,实参和形参使用的是两个不同内存中的值,即当形参的值发生改变时,不会影响实参的值,从而保证了实参数据的安全。
- 引用参数:复制参数的内存位置的引用给形式参数,即当形参的值发生改变时,同时也改变实参的值。(使用
ref关键字声明引用参数) - 输出参数,可以返回多个值。(使用
out关键字声明输出参数)
可空类型(Nullable)
- ?单问号用于对int,double,bool等无法直接赋值为null的数据类型进行null的赋值,即这个数据类型是nullable类型的
int? i = 1;<==>Nullable<int> i = new Nullable<int>(1); - ??双问号用于判断一个变量在为null的时候返回另一个指定的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// 语法
<data_type>? <variable_name> = null;
// ??
int? num1 = null;
int? num2 = 2;
int num3;
num3 = num1 ?? 3;
// 当num1为null时,num3 = 3
数组
声明
1 | datatype[] arrayName; |
初始化
- 声明一个数组不会在内存中初始化数组
- 当初始化数组变量时,您可以赋值给数组
- 数组是一个引用类型,所以需要使用
new关键字来创建数组的实例1
double[] arr = new double[3];
赋值
1 | // 使用索引号赋值给一个单独的数组元素 |
访问
1 | double[] arr = {1.1, 2.22, 3.0}; |
多维数组
- 多维数组又称为矩形数组
1
2
3
4
5// e.g:
// string变量的二维数组
string[,] names;
// int变量的三维数组
int[,,] n; - 多维数组最简单的形式就是二维数组
- 二维数组本质上是一个一维数组的列表
- 二维数组可以被认为是一个带有x行和y列的表格
- a[i, j]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// 初始化二维数组
int[,] a = new int[3, 4]{
{0, 1, 2, 3}, //初始化索引为0的行
{4, 5, 6, 7}, //初始化索引为1的行
{8, 9, 10, 11} //初始化索引为2的行
};
// 访问
int n = a[2, 3]; // = 11 (第3行第4个元素)
交错数组
- 交错数组是数组的数组
- 交错数组是一维数组
- a[ ][ ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 一个由 5 个整型数组组成的交错数组 */
int[][] a = new int[5][]{
new int[]{0, 0},
new int[]{1, 2},
new int[]{2, 4},
new int[]{3, 6},
new int[]{4, 8}
};
int i, j;
/* 输出数组中每个元素的值 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0}][{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i][j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
/* - Result:
a[0][0] = 0
a[0][1] = 0
a[1][0] = 1
a[1][1] = 2
a[2][0] = 2
a[2][1] = 4
a[3][0] = 3
a[3][1] = 6
a[4][0] = 4
a[4][1] = 8
*/
传递数组给函数
1 | using System; |
参数数组
- 参数数组通常用于传递未知数量的参数给函数
- params关键字,调用数组为形参的方法时,既可以传递数组的实参,也可以传递一组数组元素
public returnType FunName(params typeName[] arrName)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class ParamArray
{
public int AddElements(params int[] arr)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (int i in arr)
{
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
class TestClass
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ParamArray app = new ParamArray();
int sum = app.AddElements(512, 720, 250, 567, 889);
Console.WriteLine("总和是: {0}", sum);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// Output: 总和是: 2938
Array类
- 属于数组的基类,在System命名空间中定义 类属性:
- IsFixedSize: 获取一个值,该值指示数组是否带有固定大小
- IsReadOnly: 获取一个值,该值指示数组是否只读
- Length: 获取一个32位整数,该值表示所有维度的数组中的元素总数
- LongLength: 获取一个64位整数,该值表示所有维度的数组中的元素总数
- Rank: 获取数组的维度 类方法:
- Clear: 根据元素的类型,设置数组中某个范围的元素为零、为false或者为null
- Copy(Array,Array,Int32): 从数组的第一个元素开始复制某个范围的元素到另一个数组的第一个元素位置,长度由一个32位整数指定
- CopyTo(Array,Int32): 从当前的一维数组中复制所有的元素到一个指定的一维数组的指定索引位置,索引由一个32位整数指定
- GetLength: 获取一个32位整数,该值表示指定维度的数组中元素的总数
- GetLongLength: 获取一个64位整数,该值表示指定维度的数组中元素的总数
- GetLowerBound: 获取数组中指定维度的下界
- GetType: 获取当前实例的类型,从对象Object继承
- GetUpperBound: 获取数组中指定维度的上界
- GetValue(Int32): 获取一维数组中指定位置的值,索引由一个32位整数指定
- IndexOf(Array,Object): 搜索指定的对象,返回整个一维数组中第一次出现的索引
- Reverse(Array): 逆转整个一维数组中元素的顺序
- SetValue(Object, Int32): 给一维数组中指定位置的元素设置值,索引由一个32位整数指定
- Sort(Array): 使用数组的每个元素的Icomparable实现来排序整个一维数组中的元素
- ToString: 返回一个表示当前对象的字符串,从Object继承
字符串(String)
创建String对象的方法:
- 通过给String变量指定一个字符串
- 通过使用String类构造函数
- 通过使用字符串串联运算符(+)
- 通过检索属性或调用一个返回字符串的方法
- 通过格式化方法来转换一个值或对象为它的字符串表示形式类属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//字符串,字符串连接
string fname, lname;
fname = "Rowan";
lname = "Atkinson";
string fullname = fname + lname;
Console.WriteLine("Full Name: {0}", fullname);
//通过使用 string 构造函数
char[] letters = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l','o' };
string greetings = new string(letters);
Console.WriteLine("Greetings: {0}", greetings);
//方法返回字符串
string[] sarray = { "Hello", "From", "Tutorials", "Point" };
string message = String.Join(" ", sarray);
Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", message);
//用于转化值的格式化方法
DateTime waiting = new DateTime(2012, 10, 10, 17, 58, 1);
string chat = String.Format("Message sent at {0:t} on {0:D}",
waiting);
Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", chat);
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}
/* -- Output --
Full Name: RowanAtkinson
Greetings: Hello
Message: Hello From Tutorials Point
Message: Message sent at 17:58 on Wednesday, 10 October 2012
*/ - Chars: 在当前String对象中获取Char对象的指定位置
- Length: 在当前String对象中获取字符数
类方法
- public static int Compare(string strA, string strB): 比较两个指定的string对象,并返回一个表示它们在排列顺序中相对位置的整数,该方法区分大小写
- public static int Compare(string strA, string strB, bool ignoreCase): 比较两个指定的string对象,并返回一个表示它们在排列顺序中相对位置的整数,但是,如果布尔参数为真时,该方法不区分大小写
- public static string Concat(string str0, string str1): 连接两个string对象
- public static string Concat(string str0, string str1, string str2): 连接三个string对象
- public static string Concat(string str0, string str1, string str2, string str3): 连接四个string对象
- public bool Contains(string value): 返回一个表示指定string对象是否出现在字符串中的值
- public static string Copy(string str): 创建一个与指定字符串具有相同值的新的string对象
- public void CopyTo(int sourceIndex, char[] destination, int destinationIndex, int count): 从string对象的指定位置开始复制指定数量的字符到Unicode字符数组中的指定位置
- public bool EndsWith(string value): 判断string对象的结尾是否匹配指定的字符串
- public bool Equals(string value): 判断当前的string对象是否与指定的string对象具有相同的值
- public static bool Equals(string a, string b): 判断两个指定的string对象是否具有相同的值
- public static string Format(string format, Object arg0): 把指定字符串中一个或多个格式项替换为指定对象的字符串表示形式
- public int IndexOf(char value): 返回指定 Unicode 字符在当前字符串中第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始
- public int IndexOf(string value): 返回指定字符串在该实例中第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始
- public int IndexOf(char value, int startIndex): 返回指定 Unicode 字符从该字符串中指定字符位置开始搜索第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始
- public int IndexOf(string value, int startIndex): 返回指定字符串从该实例中指定字符位置开始搜索第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始
- public int IndexOfAny(char[] anyOf): 返回某一个指定的 Unicode 字符数组中任意字符在该实例中第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始
- public int IndexOfAny(char[] anyOf, int startIndex): 返回某一个指定的 Unicode 字符数组中任意字符从该实例中指定字符位置开始搜索第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始
- public string Insert(int startIndex, string value): 返回一个新的字符串,其中,指定的字符串被插入在当前 string 对象的指定索引位置
- public static bool IsNullOrEmpty(string value): 指示指定的字符串是否为 null 或者是否为一个空的字符串
- public static string Join(string separator, string[] value): 连接一个字符串数组中的所有元素,使用指定的分隔符分隔每个元素
- public static string Join(string separator, string[] value, int startIndex, int count): 连接一个字符串数组中的指定位置开始的指定元素,使用指定的分隔符分隔每个元素
- public int LastIndexOf(char value): 返回指定 Unicode 字符在当前 string 对象中最后一次出现的索引位置,索引从 0 开始
- public int LastIndexOf(string value): 返回指定字符串在当前 string 对象中最后一次出现的索引位置,索引从 0 开始
- public string Remove(int startIndex): 移除当前实例中的所有字符,从指定位置开始,一直到最后一个位置为止,并返回字符串
- public string Remove(int startIndex, int count): 从当前字符串的指定位置开始移除指定数量的字符,并返回字符串
- public string Replace(char oldChar, char newChar): 把当前 string 对象中,所有指定的 Unicode 字符替换为另一个指定的 Unicode 字符,并返回新的字符串
- public string Replace(string oldValue, string newValue): 把当前 string 对象中,所有指定的字符串替换为另一个指定的字符串,并返回新的字符串
- public string[] Split(params char[] separator): 返回一个字符串数组,包含当前的 string 对象中的子字符串,子字符串是使用指定的 Unicode 字符数组中的元素进行分隔的
- public string[] Split(char[] separator, int count): 返回一个字符串数组,包含当前的 string 对象中的子字符串,子字符串是使用指定的 Unicode 字符数组中的元素进行分隔的。int 参数指定要返回的子字符串的最大数目
- public bool StartsWith(string value): 判断字符串实例的开头是否匹配指定的字符串
- public char[] ToCharArray(): 返回一个带有当前 string 对象中所有字符的 Unicode 字符数组
- public char[] ToCharArray(int startIndex, int length): 返回一个带有当前 string 对象中所有字符的 Unicode 字符数组,从指定的索引开始,直到指定的长度为止
- public string ToLower(): 把字符串转换为小写并返回
- public string ToUpper(): 把字符串转换为大写并返回
- public string Trim(): 移除当前 String 对象中的所有前导空白字符和后置空白字符
结构体Struct
定义
- 结构体是值类型数据结构,使一个单一变量可以存储各种数据类型的相关数据
- Struct关键字用于创建结构体,用来代表一个记录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// 使用结构体定义Book的数据类型
struct Books
{
public string title;
public string author;
public string subject;
public int book_id;
};
特点
- 结构可带有方法、字段、索引、属性、运算符方法和事件
- 结构可定义构造函数,但不能定义析构函数,无参构造函数除外(默认是自动定义的,且不能被改变)
- 与类不同,结构不能继承其它的结构或类
- 结构不能作为其它结构或类的基础结构
- 结构可以实现一个或多个接口
- 结构成员不能指定为abstract、virtual或protected
- 当使用New操作符创建一个结构对象时,会调用适当的构造函数来创建结构,与类不同,结构可以不使用New操作符即可被实例化
- 如果不使用New操作符,只有在所有字段都被初始化后,字段才被赋值,对象才被使用
结构与类的不同
- 类是引用类型,在堆中分配空间,栈中保存的只是引用;结构是值类型,在栈中分配空间
- 结构不支持继承
- 结构不能声明默认的构造函数(无参构造函数)
- 结构中的构造函数,必须为所有字段赋值
- 结构中声明的字段无法赋初始值
结构与类的选择
- 当堆栈的空间很有限,且有大量的逻辑对象时,创建类要比创建结构好一些;
- 对于点、矩形和颜色这样的轻量对象,例如要声明一个含有许多个颜色对象的数组,则CLR需要为每个对象分配内存,在这种情况下,使用结构的成本较低;
- 在表现抽象和多级别的对象层次时,类是最好的选择,因为结构不支持继承。
- 大多数情况下,目标类型只是含有一些数据,或者以数据为主
枚举Enum
定义
- 枚举是一组命名整型常量,使用enum关键字声明
- 是值类型,包含自己的值,且不能继承或传递继承
语法
1 | enum <enum_name> |
类Class
定义
- 以关键字class开始,后跟类的名称
- 类的主体包含在一对花括号内
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70<access specifier> class class_name
{
// member variables
<access specifier> <data type> variable1;
<access specifier> <data type> variable2;
...
<access specifier> <data type> variableN;
// 数据类型 <data type> 指定了变量的类型
// member methods
<access specifier> <return type> method1(parameter_list)
{
// method body
// 返回类型 <return type> 指定了返回的方法返回的数据类型
}
<access specifier> <return type> method2(parameter_list)
{
// method body
}
...
<access specifier> <return type> methodN(parameter_list)
{
// method body
}
}
// 访问标识符 <access specifier> 指定了对类及其成员的访问规则
// 如果没有指定,则使用默认的访问标识符
// 类的默认访问标识符是 internal,成员的默认访问标识符是 private
// 如果要访问类的成员,你要使用点(.)运算符,点运算符链接了对象的名称和成员的名称
// e.g:
using System;
namespace BoxApplication
{
class Box
{
public double length; // 长度
public double breadth; // 宽度
public double height; // 高度
}
class Boxtester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box
Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
double volume = 0.0; // 体积
// Box1 详述
Box1.height = 5.0;
Box1.length = 6.0;
Box1.breadth = 7.0;
// Box2 详述
Box2.height = 10.0;
Box2.length = 12.0;
Box2.breadth = 13.0;
// Box1 的体积
volume = Box1.height * Box1.length * Box1.breadth;
Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}", volume);
// Box2 的体积
volume = Box2.height * Box2.length * Box2.breadth;
Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// Box1 的体积: 210
// Box2 的体积: 1560
成员函数和封装
- 成员函数是一个在类定义中有它的定义或原型的函数,就如同其它变量一样
- 作为类的成员,可以在类的任何对象上操作,且能访问该对象的类的所有成员
- 成员变量是对象的属性,且保持私有来实现封装,只能使用公共成员函数来访问
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61// e.g:
using System;
namespace BoxApplication
{
class Box
{
private double length; // 长度
private double breadth; // 宽度
private double height; // 高度
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public void setBreadth( double bre )
{
breadth = bre;
}
public void setHeight( double hei )
{
height = hei;
}
public double getVolume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
}
class Boxtester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box
Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
double volume; // 体积
// Box1 详述
Box1.setLength(6.0);
Box1.setBreadth(7.0);
Box1.setHeight(5.0);
// Box2 详述
Box2.setLength(12.0);
Box2.setBreadth(13.0);
Box2.setHeight(10.0);
// Box1 的体积
volume = Box1.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}" ,volume);
// Box2 的体积
volume = Box2.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// Box1 的体积: 210
// Box2 的体积: 1560
构造函数
- 构造函数是类的一个特殊的成员函数,当创建类的新对象时执行
- 构造函数的名称与类名完全相同,且没有任何的返回类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32using System;
namespace LineApplication
{
class Line
{
private double length; // 线条的长度
public Line()
{
Console.WriteLine("对象已创建");
}
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public double getLength()
{
return length;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Line line = new Line();
// 设置线条长度
line.setLength(6.0);
Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// 对象已创建
// 线条的长度: 6 - 默认的构造函数没有任何参数,但可以带有参数,而这样的构造函数被称为参数化构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36// e.g:
using System;
namespace LineApplication
{
class Line
{
private double length; // 线条的长度
public Line(double len) // 参数化构造函数
{
Console.WriteLine("对象已创建,length = {0}", len);
length = len;
}
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public double getLength()
{
return length;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Line line = new Line(10.0);
Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength());
// 设置线条长度
line.setLength(6.0);
Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// 对象已创建,length = 10
// 线条的长度: 10
// 线条的长度: 6
析构函数
- 析构函数是类的一个特殊的成员函数,当类的对象超出范围时执行
- 析构函数的名称是在类的名称前加上一个波浪形(~)作为前缀,没有返回值也没有任何参数
- 析构函数用于在结束程序(关闭文件、释放内存等)之前释放资源
- 析构函数不能被继承或者重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37// e.g:
using System;
namespace LineApplication
{
class Line
{
private double length; // 线条的长度
public Line() // 构造函数
{
Console.WriteLine("对象已创建");
}
~Line() //析构函数
{
Console.WriteLine("对象已删除");
}
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public double getLength()
{
return length;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Line line = new Line();
// 设置线条长度
line.setLength(6.0);
Console.WriteLine("线条的长度: {0}", line.getLength());
}
}
}
// 对象已创建
// 线条的长度: 6
// 对象已删除
静态成员
- 使用
static关键字将类成员定义为静态的,即类中只有一个该成员的实例 - 静态变量用于定义常量,可以直接调用类而不需要创建类的实例来获取
- 静态变量可以在成员函数或类的定义外部进行初始化,也可以在类的定义内部初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36// e.g:
using System;
namespace StaticVarApplication
{
class StaticVar
{
public static int num;
public void count()
{
num++;
}
public int getNum()
{
return num;
}
}
class StaticTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
StaticVar s1 = new StaticVar();
StaticVar s2 = new StaticVar();
s1.count();
s1.count();
s1.count();
s2.count();
s2.count();
s2.count();
Console.WriteLine("s1 的变量 num: {0}", s1.getNum());
Console.WriteLine("s2 的变量 num: {0}", s2.getNum());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// s1 的变量 num: 6
// s2 的变量 num: 6 - 可以将一个成员函数声明为static,该函数只能访问静态变量
- 静态函数在对象被创建之前就已经存在
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30// e.g:
using System;
namespace StaticVarApplication
{
class StaticVar
{
public static int num;
public void count()
{
num++;
}
public static int getNum()
{
return num;
}
}
class StaticTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
StaticVar s = new StaticVar();
s.count();
s.count();
s.count();
Console.WriteLine("变量 num: {0}", StaticVar.getNum());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// 变量 num: 3
继承
- 继承允许根据一个类来定义另一个类
- 设计一个新的类,继承已有的类的成员,已有的类被称为基类,新的类被称为派生类
基类和派生类
- 一个类可以派生多个类或者接口,即可以从多个基类或者接口继承数据和函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53// 语法:
<访问修饰符> class <基类>
{
...
}
class <派生类> : <基类>
{
...
}
// e.g:
using System;
namespace InheritanceApplication
{
class Shape
{
public void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
public void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected int width;
protected int height;
}
// 派生类
class Rectangle: Shape
{
public int getArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
}
class RectangleTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle Rect = new Rectangle();
Rect.setWidth(5);
Rect.setHeight(7);
// 打印对象的面积
Console.WriteLine("总面积: {0}", Rect.getArea());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// 总面积: 35
基类的初始化
由于派生类继承了基类的成员变量和成员方法,所以父类对象应在子类对象创建之前被创建
1 | // e.g: |
多重继承
指一个类同时从多个父类继承,但C#不支持多重继承,需要使用接口来实现
1 | // e.g: |
多态
- 多态是同一个行为具有多个不同表现形成或形态的能力
- 一般在面向对象的编程中,多态表现为:一个接口,多个功能
- 多态可以是静态的或动态的
- 静态多态中,函数的响应是在编译时发生的
- 动态多态中,函数的响应是在运行时发生的
- 每个类型都是多态的,因为所有类型都继承自Object
静态多态
两种技术实现静态多态:
- 函数重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70// 可以在同一个范围内对相同的函数名有多个定义
// 函数的定义必须彼此不同,可以是参数列表中的参数类型不同,也可以是参数个数不同
// 不能重载只有返回类型不同的函数声明
// e.g:
// 参数个数不同
using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
public class TestData
{
public int Add(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestData dataClass = new TestData();
int add1 = dataClass.Add(1, 2);
int add2 = dataClass.Add(1, 2, 3);
Console.WriteLine("add1 :" + add1);
Console.WriteLine("add2 :" + add2);
}
}
}
// 参数类型不同
using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
class Printdata
{
void print(int i)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出整型: {0}", i );
}
void print(double f)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出浮点型: {0}" , f);
}
void print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出字符串: {0}", s);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Printdata p = new Printdata();
// 调用 print 来打印整数
p.print(1);
// 调用 print 来打印浮点数
p.print(1.23);
// 调用 print 来打印字符串
p.print("Hello Runoob");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// 输出整型: 1
// 输出浮点型: 1.23
// 输出字符串: Hello Runoob - 运算符重载Tips:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83// 可以重定义或重载C#中内置的运算符
// 重载运算符是具有特殊名称的函数,是通过关键字`operator`后跟运算符的符号来定义的
// 与其它函数一样,重载运算符有返回类型和参数列表
// e.g:
using System;
namespace OperatorOvlApplication
{
class Box
{
private double length; // 长度
private double breadth; // 宽度
private double height; // 高度
public double getVolume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public void setBreadth( double bre )
{
breadth = bre;
}
public void setHeight( double hei )
{
height = hei;
}
// 重载 + 运算符来把两个 Box 对象相加
public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.length = b.length + c.length;
box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth;
box.height = b.height + c.height;
return box;
}
}
class Tester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box
Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
Box Box3 = new Box(); // 声明 Box3,类型为 Box
double volume = 0.0; // 体积
// Box1 详述
Box1.setLength(6.0);
Box1.setBreadth(7.0);
Box1.setHeight(5.0);
// Box2 详述
Box2.setLength(12.0);
Box2.setBreadth(13.0);
Box2.setHeight(10.0);
// Box1 的体积
volume = Box1.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}", volume);
// Box2 的体积
volume = Box2.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume);
// 把两个对象相加
Box3 = Box1 + Box2;
// Box3 的体积
volume = Box3.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box3 的体积: {0}", volume);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// Box1 的体积: 210
// Box2 的体积: 1560
// Box3 的体积: 5400 - 可被重载的运算符:一元运算符(+, -, !, ~, ++, –),二元运算符(+, -, *, /, %),比较运算符(==, !=, <, >, <=, >=)
- 不可被重载的运算符:条件逻辑运算符(&&, ||),赋值运算符(+=, -=, *=, /=, %=),(=, ., ?:, ->, new, is, sizeof, typeof)
动态多态
- 使用关键字
abstract创建抽象类,用于提供接口的部分类的实现 - 当一个派生类继承自该抽象类时,实现即完成
- 抽象类包含抽象方法,可以被派生类实现
- 不能创建抽象类的实例,不能在一个抽象类外部声明一个抽象方法
- 通过关键字
sealed可以将类声明为密封类,此时该类不能被继承,且抽象类不支持该声明1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
abstract class Shape
{
abstract public int area();
}
class Rectangle: Shape
{
private int length;
private int width;
public Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0)
{
length = a;
width = b;
}
public override int area ()
{
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle 类的面积:");
return (width * length);
}
}
class RectangleTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 7);
double a = r.area();
Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}",a);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
// Rectangle 类的面积:
// 面积: 70 - 当一个定义在类中的函数需要在继承类中实现时,可以使用虚方法
- 虚方法的关键字是
virtual声明 - 虚方法可以在不同的继承类中有不同的实现
- 对虚方法的调用是在运行时发生的
- 动态多态是通过抽象类和虚方法实现的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71// e.g:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Shape
{
public int X { get; private set; }
public int Y { get; private set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public int Width { get; set; }
// 虚方法
public virtual void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("执行基类的画图任务");
}
}
class Circle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("画一个圆形");
base.Draw();
}
}
class Rectangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("画一个长方形");
base.Draw();
}
}
class Triangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("画一个三角形");
base.Draw();
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建一个 List<Shape> 对象,并向该对象添加 Circle、Triangle 和 Rectangle
var shapes = new List<Shape>
{
new Rectangle(),
new Triangle(),
new Circle()
};
// 使用 foreach 循环对该列表的派生类进行循环访问,并对其中的每个 Shape 对象调用 Draw 方法
foreach (var shape in shapes)
{
shape.Draw();
}
Console.WriteLine("按下任意键退出。");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// 画一个长方形
// 执行基类的画图任务
// 画一个三角形
// 执行基类的画图任务
// 画一个圆形
// 执行基类的画图任务
接口Interface
定义
接口定义了所有类继承接口时应遵循的语法合同,接口定义了语法合同“是什么”部分,派生类定义了语法合同“怎么做”部分。
- 接口定义了属性、方法和事件,都属于接口成员,且只包含了成员的声明
- 成员的定义是派生类的责任,接口只提供派生类应遵循的标准结构
- 使实现接口的类或结构在形式上保持一致
- 抽象类在某种程度上与接口类似,但大多只用在当只有少数方法由基类声明由派生类实现时
- 接口本身并不实现任何功能,只是和声明实现该接口的对象订立一个必须实现哪些行为的契约
- 抽象类不能直接实例化,但允许派生具体的具有实际功能的类
- 接口使用
interface关键字声明,与类的声明相似,默认为public修饰 - 接口通常以字母
I开头
接口的实现
1 | using System; |
接口的继承
- 如果一个接口继承了其它接口,那么实现类或结构就需要实现所有接口的成员,即子接口和父接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36// e.g:
using System;
// 父接口
interface IParentInterface
{
void ParentInterfaceMethod();
}
// 子接口,继承自IParentInterface
interface IMyInterface : IParentInterface
{
void MethodToImplement();
}
// 实现类 - 继承子接口
class InterfaceImplementer : IMyInterface
{
static void Main()
{
InterfaceImplementer iImp = new InterfaceImplementer();
iImp.MethodToImplement();
iImp.ParentInterfaceMethod();
}
// 实现子接口的成员方法
public void MethodToImplement()
{
Console.WriteLine("MethodToImplement() called.");
}
// 实现子接口的父接口的成员方法
public void ParentInterfaceMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("ParentInterfaceMethod() called.");
}
}
// MethodToImplement() called.
// ParentInterfaceMethod() called.
命名空间Namespace
作用:提供一种让一组名称与其它名称分隔开的方式,即在一个命名空间中声明的类的名称与另一个命名空间中声明的相同的类的名称不冲突
定义
- 命名空间以
namespace关键字声明,后加命名空间的名字1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43namespace namespace_name
{
// 代码声明
}
// 调用支持命名空间版本的函数或变量,命名空间的名称要前置
namespace_name.item_name;
// e.g:
using System;
namespace first_space
{
class namespace_cl
{
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("Inside first_space");
}
}
}
namespace second_space
{
class namespace_cl
{
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("Inside second_space");
}
}
}
class TestClass
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
first_space.namespace_cl fc = new first_space.namespace_cl();
second_space.namespace_cl sc = new second_space.namespace_cl();
fc.func();
sc.func();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// Inside first_space
// Inside second_space
关键字using
- 表明程序使用的是给定命名空间中的名称
- 使用using命名空间指令,就可以不用在前面加上命名空间名称
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37using System;
using first_space;
using second_space;
namespace first_space
{
class abc
{
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("Inside first_space");
}
}
}
namespace second_space
{
class efg
{
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("Inside second_space");
}
}
}
class TestClass
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
abc fc = new abc();
efg sc = new efg();
fc.func();
sc.func();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// Inside first_space
// Inside second_space - using static: 指定无需指定类型名称即可访问其静态成员的类型
1
2
3using static System.Math;
var = PI;
// 直接使用System.Math.PI - 起别名:
using Project = PC.MyCompany.Project; - 若使用using指令,则省略命名空间名称后的类方法调用不能同名,否则会报错
嵌套命名空间
- 命名空间可以被嵌套,即在一个命名空间内定义另一个命名空间
- 可以使用(.)运算符访问嵌套的命名空间的成员
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40// 语法:
namespace namespace_name1
{
// 代码声明
namespace namespace_name2
{
// 代码声明
}
}
// e.g:
using System;
using SomeNameSpace;
using SomeNameSpace.Nested;
namespace SomeNameSpace
{
public class MyClass
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("In SomeNameSpace");
Nested.NestedNameSpaceClass.SayHello();
}
}
// 内嵌命名空间
namespace Nested
{
public class NestedNameSpaceClass
{
public static void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("In Nested");
}
}
}
}
// In SomeNameSpace
// In Nested
预处理器指令
- 指导编译器在实际编译开始之前对信息进行预处理
- 所有的预处理器指令都以
#开始,且在一行上,只有空白字符可以出现在预处理器指令之前 - 预处理器指令不属于语句,所以不以分号结束
可用的预处理器指令
- #define:用于定义一系列成为符号的字符
- #undef:用于取消定义符号
- #if:用于测试符号是否为真
- #else:用于创建复合条件指令,与#if一起使用
- #endif:用于指定一个条件指令的结束
- #line:用于修改编译器的行数以及(可选的)输出错误和警告的文件名
- #error:用于允许从代码的指定位置生成一个错误
- #warning:用于允许从代码的指定位置生成一级警告
- #region:用于在使用Visual Studio Code Editor的大纲特性时,指定一个可展开或折叠的代码块
- #endregion:用于标识#region块的结束
正则表达式
定义
- 字符转义
- 字符类
- 定位点
- 分组构造
- 限定符
- 反向引用构造
- 备用构造
- 替换
- 杂项构造
Regex类
- public bool IsMatch(string input): 指示 Regex 构造函数中指定的正则表达式是否在指定的输入字符串中找到匹配项
- public bool IsMatch(string input, int startat): 指示 Regex 构造函数中指定的正则表达式是否在指定的输入字符串中找到匹配项,从字符串中指定的开始位置开始
- public static bool IsMatch(string input, string pattern): 指示指定的正则表达式是否在指定的输入字符串中找到匹配项
- public MatchCollection Matches(string input): 在指定的输入字符串中搜索正则表达式的所有匹配项
- public string Replace(string input, string replacement): 在指定的输入字符串中,把所有匹配正则表达式模式的所有匹配的字符串替换为指定的替换字符串
- public string[] Split(string input): 把输入字符串分割为子字符串数组,根据在 Regex 构造函数中指定的正则表达式模式定义的位置进行分割
异常处理
- 异常是在程序执行期间出现的问题,对程序运行时出现的特殊情况的一种响应
- 异常提供了一种把程序控制权从某个部分转移到另一个部分的方式
四个关键字:
- try: 一个 try 块标识了一个将被激活的特定的异常的代码块,后跟一个或多个 catch 块。
- catch: 程序通过异常处理程序捕获异常,catch 关键字表示异常的捕获。
- finally: finally块用于执行给定的语句,不管异常是否被抛出都会执行。
- throw: 当问题出现时,程序抛出一个异常,使用 throw 关键字来完成。
语法
1 | try |
异常类
- 主要是直接或者间接的派生于System.Exception类,例如:System.ApplicationException 和 System.SystemException 类
- System.ApplicationException 类支持由应用程序生成的异常,即自定义的异常都应派生自该类
- System.SystemException 类是所有预定义的系统异常的基类
System.SystemException 类的预定义的异常类:
- System.IO.IOException: 处理 I/O 错误
- System.IndexOutOfRangeException: 处理当方法指向超出范围的数组索引时生成的错误
- System.ArrayTypeMismatchException: 处理当数组类型不匹配时生成的错误
- System.NullReferenceException: 处理当依从一个空对象时生成的错误
- System.DivideByZeroException: 处理当除以零时生成的错误
- System.InvalidCastException: 处理在类型转换期间生成的错误
- System.OutOfMemoryException: 处理空闲内存不足生成的错误
- System.StackOverflowException: 处理栈溢出生成的错误
异常处理
1 | // 当除以零时抛出异常的实例: |
自定义异常
1 | // e.g: |
抛出对象
- 如果异常是直接或间接派生自 System.Exception 类,可以在 catch 块中使用 throw 语句来抛出当前的对象
1
2
3
4
5Catch(Exception e)
{
...
Throw e
}
文件的操作
- 一个文件是一个存储在磁盘中带有指定名称和目录路径的数据集合,当打开文件进行读写时,它变成一个流,即流是通过通信路径传递的字节序列
- 有两个主要的流:输入流和输出流
- 输入流用于从文件读取数据(读操作)
- 输出流用于向文件写入数据(写操作)
I/O类
System.IO 命名空间有各种不同的类,用于执行各种文件操作,如创建和删除文件、读取或写入文件,关闭文件等。
常用的非抽象类:
- BinaryReader:从二进制流读取原始数据。
- BinaryWriter:以二进制格式写入原始数据。
- BufferedStream:字节流的临时存储。
- Directory:有助于操作目录结构。
- DirectoryInfo:用于对目录执行操作。
- DriveInfo:提供驱动器的信息。
- File:有助于处理文件。
- FileInfo:用于对文件执行操作。
- FileStream:用于文件中任何位置的读写。
- MemoryStream:用于随机访问存储在内存中的数据流。
- Path:对路径信息执行操作。
- StreamReader:用于从字节流中读取字符。
- StreamWriter:用于向一个流中写入字符。
- StringReader:用于读取字符串缓冲区。
- StringWriter:用于写入字符串缓冲区。
FileStream类
- System.IO 命名空间中的 FileStream 类有助于文件的读写与关闭,该类派生自抽象类Stream例子参考
1
2
3
4
5// 创建FileStream对象的语法:
FileStream <object_name> = new FileStream( <file_name>,
<FileMode Enumerator>, <FileAccess Enumerator>, <FileShare Enumerator>);
// 创建一个 FileStream 对象 F 来读取名为 sample.txt 的文件
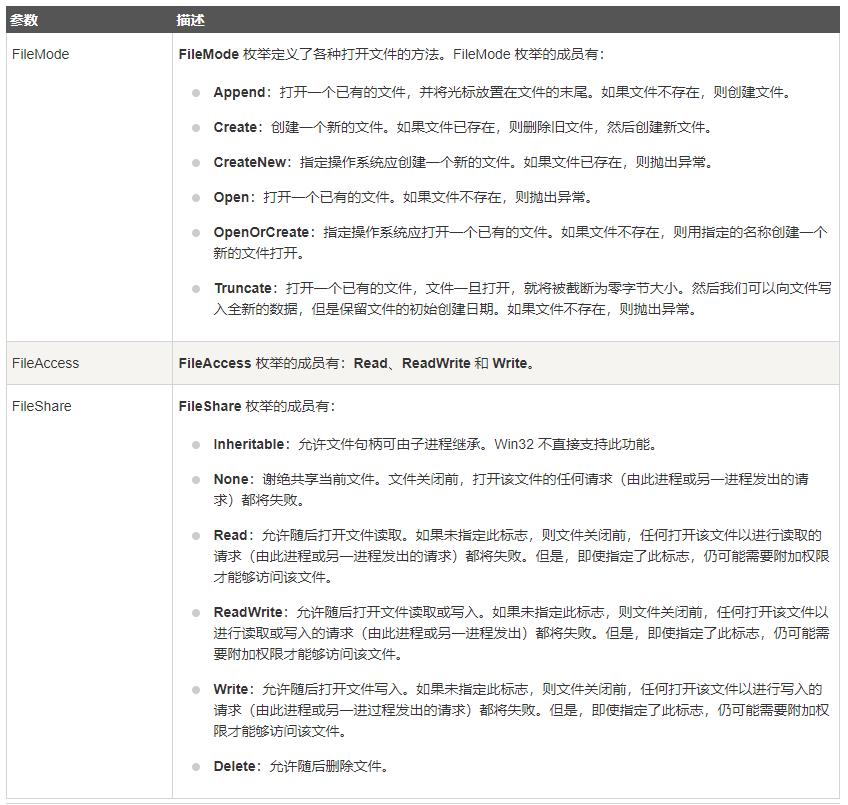
FileStream F = new FileStream("sample.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read); - FileMode: Append | Create | CreateNew | Open | OpenOrCreate | Truncate
- FileAccess: Read | ReadWrite | Write
- FileShare: Inheritable | None | Read | ReadWrite | Write | Delete
1 | using System; |
高级文件操作
文本文件的读写:涉及文本文件的读写,StreamReader 和 StreamWriter 类
二进制文件的读写:涉及到二进制文件的读写,BinaryReader 和 BinaryWriter 类
Windows文件系统的操作:浏览并定位 Windows 文件和目录